Home ->
Medical Education ->
Simulators -> Anesthesia -> Airway Management -> Difficult Airway Management Simulator -Training Model
- Difficult Airway Management Simulator offers unprecedented experience in DAM training with wide varieties of settings.
- Accurate anatomy and realistic feeling of airway will meet requirements of all levels of trainees.
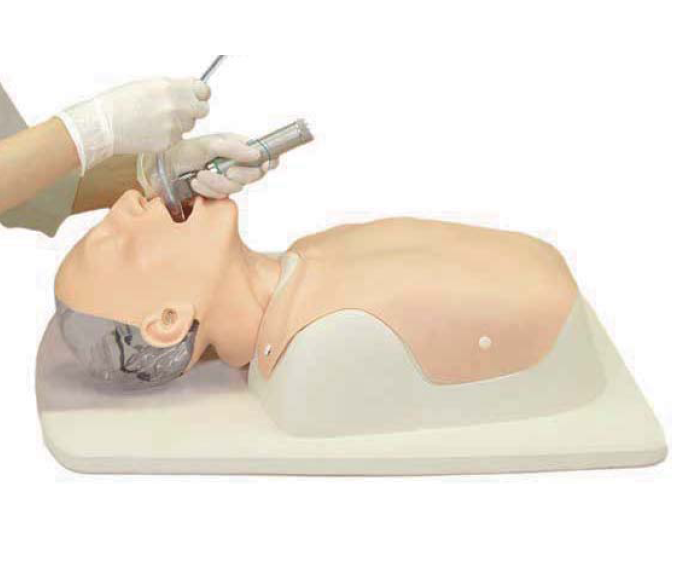
- True-to-life articulation allows for head-tilt/chin-lift and jaw-thrust techniques.
- Once the head is set at "sniffing position", intubation with laryngoscope can be performed.
- The placement of the tube can be confirmed by auscultation or movement of thoracoabdominal area.
- A Variety of Possible Airway Skills including Intubation with a laryngoscope, BVM ventilation, nasal intubation, Laryngeal mask ventilation, and use of a video laryngoscope.
- The incisors are removable when excessive force is applied.
- 24 variations of patient scenario (including 1 normal case): 3 stages of mouth opening, 2 stages of neck flexibility, 2 tongue sizes
- and 2 positions of the vocal cord.
-
Variation of DAM Setting:
- Neck flexibility: Life-like jaw movement (Normal / Rigid).
- Mouth Opening: Normal / Intermediate / Difficult.
- Tongue: Normal / Swollen.
- Laryngospasm: Normal / Laryngospasm.
- Available with an optional bronchofiberscopy training unit (sold separately).
Set Include:
- 1 manikin
- 3 upper incisors
- 1 lubricant
- 1syringe
- 1 carrying bag
- 1 instruction manual
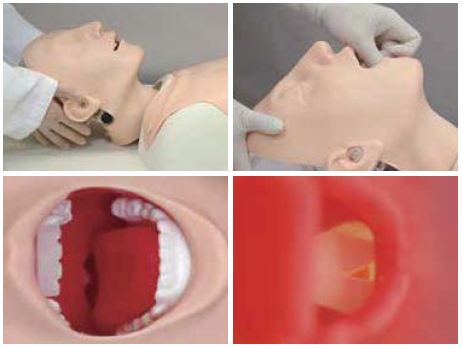
- Airway opening techniques (head tilt, jaw thrust).
- Bag-Valve-Mask ventilation.
- Pre-intubation airway assessment
- "Sniffing position"
- Pressurization of external larynx to improve the laryngeal view
- Intraoral/Intranasal Intubation
- Use of oropharyngeal airway (OPA)
- Use of nasopharyngeal airway (NPA)
- Use of laryngeal mask airway
- Use of video laryngeal scope
-
Confirmation of successful ventilation by:
- Observation of thoracic and abdominal movement (lung expansion, stomach inflation) or
- Auscultation of the chest
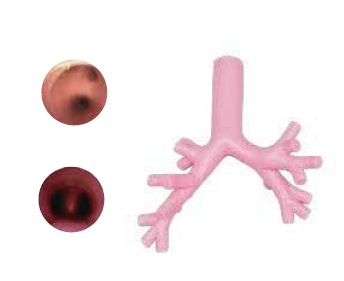
- Feedback of incorrect procedures including esophagus intubation and unilateral intubation
- Securing the tube in place with tape or Thomas™ endotracheal tube holder